UNDERSTANDING GYNECOMASTIA:
CAUSES, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENT
Gynecomastia, a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males, affects a significant number of men worldwide. While it can cause physical discomfort and psychological distress, understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help individuals make informed decisions and seek appropriate medical care. In this article, we will delve into the details of gynecomastia, shedding light on its causes and outlining the various treatment options available.
Gynecomastia, what is it ?
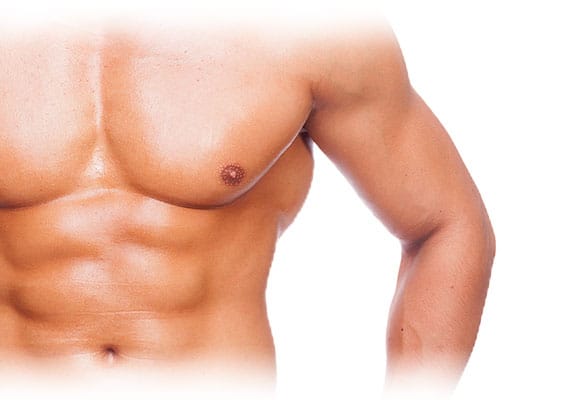
Gynecomastia is the abnormal enlargement of breast tissue in males, resulting in the appearance of breasts. Although commonly associated with hormonal imbalances, it can also occur due to other factors such as obesity, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts and can range from a small amount of tissue growth to more pronounced enlargement.
Causes of Gynecomastia:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly a relative increase in estrogen levels compared to testosterone, can lead to gynecomastia. This imbalance can occur during puberty, aging, or due to certain medical conditions, such as hypogonadism or hyperthyroidism.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can contribute to the development of gynecomastia. Adipose tissue (fat cells) produces estrogen, which can disrupt the hormonal balance and lead to breast tissue enlargement.
- Medications and Substances: Certain medications and substances have been associated with gynecomastia. These include anabolic steroids, anti-androgens, some anti-depressants, calcium channel blockers, and marijuana, among others.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Some medical conditions, such as liver disease, kidney failure, tumors, and genetic disorders, can contribute to gynecomastia by affecting hormone production or metabolism.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
The primary symptom of gynecomastia is the presence of enlarged breast tissue. Other signs may include tenderness or sensitivity in the breast area. It is important to note that gynecomastia is different from pseudogynecomastia, which refers to an increase in breast size due to excess fat without the presence of glandular tissue.
To diagnose gynecomastia, a physical examination and review the individual’s medical history is needed. In some cases, further tests, such as blood work, hormone level evaluations, or imaging studies, may be recommended to identify the underlying cause.
Treatment Options:
- Observation: In cases where gynecomastia is caused by temporary hormonal imbalances during puberty, it often resolves on its own over time. In such cases, observation and regular monitoring by a healthcare professional may be sufficient.
- Lifestyle Modifications: For individuals with gynecomastia associated with obesity, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise and a balanced diet may help reduce excess body fat and improve the condition.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) or aromatase inhibitors, may be prescribed to reduce breast tissue growth or alleviate symptoms in some cases. However, medication effectiveness can vary, and their use should be carefully monitored by a healthcare professional.
-
 SURGERY: IN CASES WHERE GYNECOMASTIA PERSISTS OR CAUSES SIGNIFICANT PHYSICAL OR PSYCHOLOGICAL DISTRESS, SURGICAL INTERVENTION MAY BE CONSIDERED. SURGICAL OPTIONS INCLUDE LIPOSUCTION TO REMOVE EXCESS FAT, EXCISION TO REMOVE GLANDULAR TISSUE, OR A COMBINATION OF BOTH. IT IS IMPORTANT TO CONSULT WITH A QUALIFIED PLASTIC SURGEON TO DISCUSS THE POTENTIAL RISKS, BENEFITS, AND EXPECTED OUTCOMES OF THE PROCEDURE.
SURGERY: IN CASES WHERE GYNECOMASTIA PERSISTS OR CAUSES SIGNIFICANT PHYSICAL OR PSYCHOLOGICAL DISTRESS, SURGICAL INTERVENTION MAY BE CONSIDERED. SURGICAL OPTIONS INCLUDE LIPOSUCTION TO REMOVE EXCESS FAT, EXCISION TO REMOVE GLANDULAR TISSUE, OR A COMBINATION OF BOTH. IT IS IMPORTANT TO CONSULT WITH A QUALIFIED PLASTIC SURGEON TO DISCUSS THE POTENTIAL RISKS, BENEFITS, AND EXPECTED OUTCOMES OF THE PROCEDURE.


